mushroom life cycle explained
Once these spores germinate they start to grow a fine filament called hyphaeWhen multiple hyphae are growing together they form a network that is called. Not so to cultivators.

Lion S Mane A Psychosomatic Psychobiotic Reishi And Roses Decrease Inflammation Antigen Presenting Cell Lipid Peroxidation
Moreover mushrooms begin fruiting in 5-7 days.

. A small mushroom can produce more than a million spores which can be carried by the. The process is easy to understand if you look at it one step at a time. At first its cap will remain closed and is sometimes covered by a veil.
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction. After mushroom spawn is mixed with the substrate youll notice mycelium in 10-14 days. Spores alight upon a growth medium.
Learn more about the mushroom life cycle and enjoy a timelapse video of oyster mushrooms growing. Primordia formation growth mushroom mature drops spores. These components are called basidium and it is right on the outside of the small tips of the end of the basidium that the spores will appear.
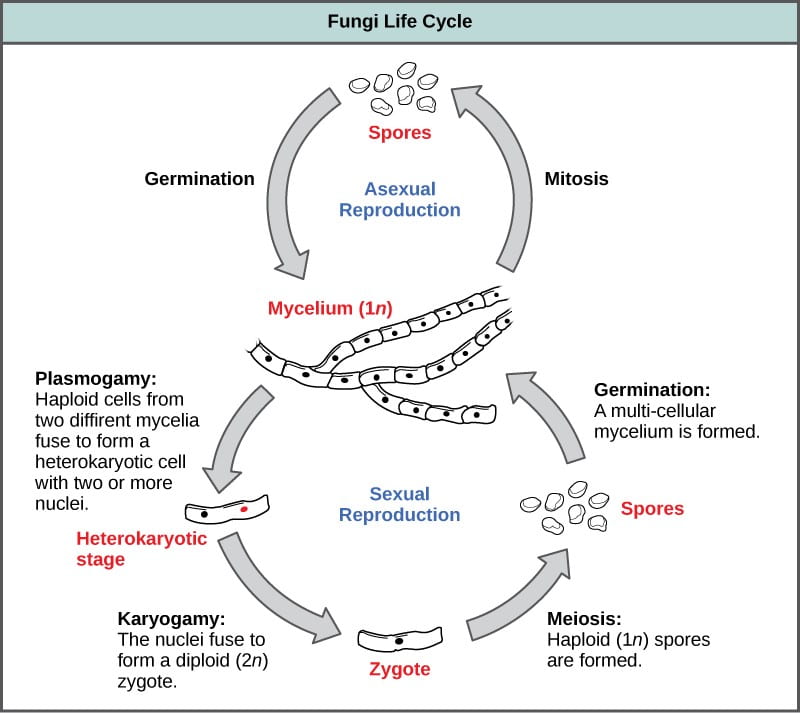
The Mushroom Life Cycle. A mushroom matures in stages. Most of the mushroom life cycle is hidden from us but here are the steps as we understand them.
Now locate the club-shaped structures of the plant. The Life Cycle of Mushrooms. Various stage of mushroom development right and mature.
The oyster mushroom cycle of life is relatively quick. The earliest recognizable stage of an organism as it develops in this case a mushroom. The lamellae are covered with numerous microscopic protuberances called basidia which produce and release spores completing the life cycle of the fungus.
They meet compatible spores. Theyre easy to grow delicious and very healthy. Because mushrooms are a fungus and not.
This article will focus on Basidiomycetes a class of fungi that includes gilled mushrooms polypores puffballs boletes and more. The following is a typical life cycle of a mushroom-forming Basidiomycete. However most varieties follow a somewhat similar pattern which we will describe below.
Spores are the reproductive unit of the mushroom and are released from the gills and pores. Hundreds of thousands of spores are released from under a grown mushrooms cap. Mushrooms dont have seeds like plants.
These spores are released from the gills underneath the cap of the mushroom. The mycelium the body or roots of the mushroom grows through this substrate and excretes enzymes to convert it into an absorbable form. A mature mushroom drops spores.
Mushrooms are a kind of fungus. The spores that drop to the ground comes from mature mushrooms. For illustrative purposes you can think of spores as the seeds.
This tutorial illustrates the relationships among these phases in the life cycle of a mushroom. As the mushroom grows and opens the veil protecting the underside of the cap breaks exposing the gills. Lower temperatures can help increase condensation on the spores.
Three ecological roles within the mushroom life cycle. Spore germination colonisation fruiting and sporulation. The first sign of an emerging mushroom is a hyphal knot.
Mycelium originates pinheads originate. The mushroom part we can see above ground is actually just the reproductive body of the fungus at large. The mushroom cultivator follows the path of the mushroom life cycle.
The dikaryotic phase in which cells in a fun-gal mycelium have two nuclei. A phase of life that is unique to fungi. This primordia is visible to the naked eye which means all the hard work is about to pay off.
There are four basic stages to the life cycle of a mushroom. At the beginning of the life cycle of mushrooms it starts off as spores. The mushroom basidiocarp is typically composed of a stipe that elevates the basidiocarp above the substrate a pileus and in some species a partial veil that encloses and protects the lamella as the basidia and basidiospores are developing Fig 1-2.
Heres how the mushroom life cycle works. These spores are commonly referred to as basidiospores. The Mushroom Life Cycle explained Spore Dropping Process Spores are like mushroom seeds.
Mycorrhizal fungi form beneficial partnerships with plants and trees trading water and nutrients for carbohydrates and sugars. Theyre the pre-baby stage of a mushroom life cycle and are asexual meaning theyre all the same theres no female or male spores as can occur in some plants. Spores fall on the ground spores germinate.
Mushrooms are a kind of fungus that usually look like umbrellas and grow in places like yards forests fields and gardens. The life of a mushroom begins with a spore. Growing into hyphae Spores begin to divide and produce hyphae once they land in the right habitat.
The spores which are so small they cant be seen by the naked eye are male or. Release of spores birth As we mentioned above a mature mushroom will release its spores as a way of reproducing. A Hypha is a long thread that branches out of a germinated spore.
Another type of mushroom you may enjoy growing is the oyster mushroom. It then germinates dividing by mitosis to produce a thread like fiber called the Hypha. The mycelium will grow through its environment.
Spores are the reproductive cells of fungi. The mushroom life cycle remains largely invisible to most mushroom hunters. Learning Objectives Know the structures involved in.
These fungi not only extend the root zone but they also link together different trees and tree species to exchange. 1- A haploid spore lands in a suitable habitat germinates and forms monokaryotic primary mycelium. There are typically four produced at the end of each basidium.
Over 80 of plants have mycorrhizal partners. Ballistosporys requirement for moisture may explain why mushroom flesh is notably cool. Fruitbodies form only at the completion of the mushroom life cycle and for most species occur but for a few days then disappear.
In general for the cultivator this means to. As it grows the cap flattens out and the veil breaks possibly leaving a ring on the stipe. This is when mycelium comes together to form a knot near the surface of the soil which will soon develop into a primordia aka baby mushroom cute.
Once it is fully developed the reproductive surface curves upward exposing the. A mushroom forms with all its required parts stem cap gills for example in the most early stages of life meaning it is pre-formed and if damaged while young those defects will show up in the mature mushroom. It produces billions of spores kind of like seeds or pollen that are spread throughout the environment.
In this stage of the mushroom life cycle the mycelium takes control finding nutrients to break down for the mushroom fueling its exponential growth it also acts as the mushrooms immune system repelling competitors and predators with protective compounds and enzymes. The mushroom life cycle varies slightly from species to species.

The Mushroom Life Cycle Forest Origins

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle

The Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Teelixir

The Science Of Mushroom Anatomy Mycelium The Fruitbody Fungi Perfecti

The Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Teelixir

The Mushroom Life Cycle Forest Origins

Dr Danny Haelewaters Stands With Ukraine On Twitter Plant Fungus Slime Mould Stuffed Mushrooms

Life Cycle And Lifespan Of Giant Millipedes Explained Keeping Bugs Life Cycles Millipede Life Cycle Stages

Sorting And Classifying Plants And Animals View As Single Page Teaching Biology Science For Kids Science And Nature

Growing Mushrooms From Mushrooms Sporeshift Nz
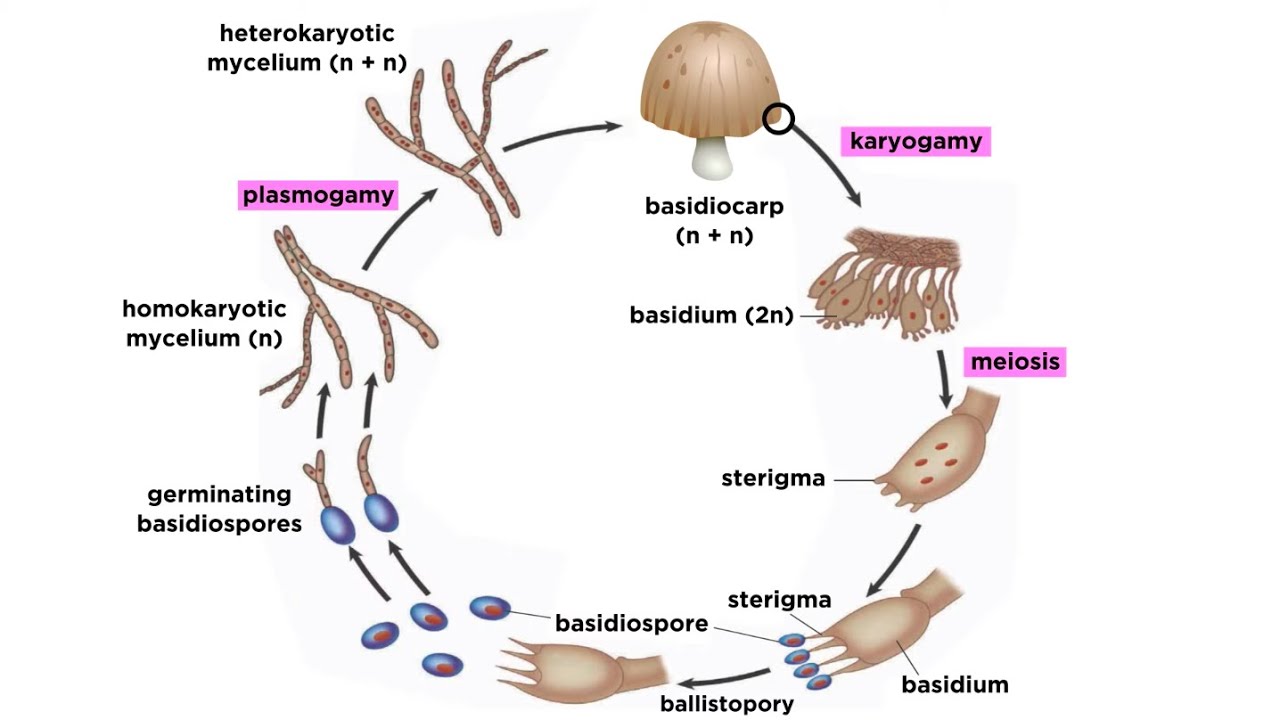
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube

Healthy Soil Teems With Bacteria Fungi Viruses And Other Microorganisms That Help Store Carbon And Fend Off Plant Diseases T Food Web Compost Tea Arthropods

The Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Natura Mushrooms

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Cyathus Novaezelandiae Booyong N S Wales Australia The Bird S Nest Fungi Family Have Widespread Distribution Stuffed Mushrooms Fungi Magical Mushrooms

Magic Mushrooms Explained Doubleblind Mag

Mushroom Life Cycle Learn All You Need To Know Here Stuffed Mushrooms Scientific Illustration Life Cycles
Medicinal Mushrooms The Mycelium Vs Fruiting Body Dispute North Spore